Myositis is a condition that causes pain in the muscles. This disease occurs when the muscle fibers in a person’s body begin to break down very quickly. This leads to a release of the materials in the muscle fibers into the blood. These materials can harm the kidneys and cause severe pain, swelling and weakness in the muscles. The most common cause of myositis is viral infection. Bacteria can also cause myositis. The viruses attack muscle tissue directly, releasing substances that damage the muscle tissues.
There are a variety of different treatments available for myositis. Some patients experience symptoms for several weeks to months after infection. Medications for the condition include steroids, physical therapy, and heat therapy. However, treatment for this disease can vary. There is no cure for this disease, so it is essential to seek treatment as soon as possible. You will need to work with your doctor to determine the right treatment for your specific case.
The first step in treating myositis is to determine what is causing it. It is important to seek medical attention if the muscle symptoms are caused by any autoimmune disorder. Your doctor may be able to rule out the causes of myositis by comparing your blood work with those of others. In some cases, medications that cause inflammation of the muscle will be ineffective, so it is best to seek medical attention immediately.
Reactive myositis is an inflammatory type of myositis in which the muscle cells are damaged and destroyed. Those with this disease find it difficult to walk and use their arms. Reactive myositis is often triggered by statin medications. Occasionally, it can occur after a viral infection. If the condition is not treated early, it can lead to more severe symptoms.
Symptoms of myositis generally peak 5 to 6 weeks after an infection. The disease typically resolves completely after about six months, but the rash and muscle pain may persist for a few more weeks. A healthcare provider will be able to identify the source of the infection and prescribe a course of treatment. Acute myositis is a serious condition with a poor outlook. If diagnosed early, myositis can be treated and the symptoms will subside without any further problems.
Myositis is caused by a bacterial infection. Candida is the most common type of Candida species that causes this disease. Fungal myositis is usually accompanied by a rash and fever. It is characterized by pain in the limbs and can affect the joints. Some patients may even develop an acute infection. The symptoms of myositis can range from mild to severe and range from temporary to permanent.
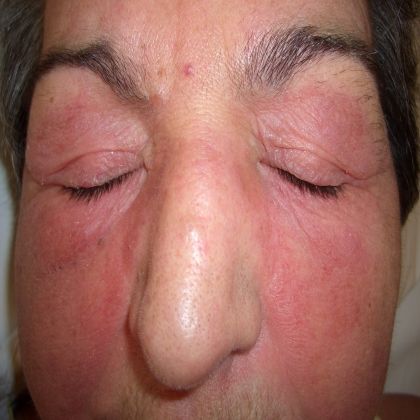
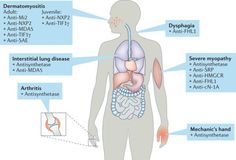
The most common way to diagnose myositis is to conduct blood tests. Blood tests can identify muscle damage. The most common symptoms include pain in the muscles, symmetrical weakness, and joint pain. Dysphagia (the abnormal movement of food) and weight loss are other symptoms of autoimmune myositis. A diagnosis of myositis is usually made by the doctor’s diagnosis.
The symptoms of myositis are similar to those of other types of diseases. The most common symptoms are fatigue, muscle pain and muscle weakness. Fortunately, it responds well to treatment. Prevention strategies include reducing risk factors, preventing the condition, and treating the condition. The condition can even be cured with exercise, proper nutrition, and sanitation. If left untreated, myositis can become permanent.
Treatment for myositis depends on the underlying cause of the disease. Most treatments are based on immunosuppression and physiotherapy. Some non-drug therapies can help patients maintain strength and avoid complications. These methods may not be effective, so on the site https://handaldok.com/
you can get acquainted with natural preparations that experts can recommend and choose the appropriate treatment for yourself. Many medicines are not recommended for myositis. In addition to antibiotics, the disease is also associated with liver infection.
There are various causes of myositis. Muscle inflammation is a common cause, but it can also be caused by other factors such as medications. The most common cause of myositis is a viral infection. Infections can also cause muscle inflammation. HIV can cause myositis, and adenovirus can also be a source of autoimmune disease.

Leave a Reply